How to use PUJI OMS
PUJI, an OMS of First Capital Securities Limited, is one of the best free stock trading app in Bangladesh. It’s the most trust worthy stock market trading & investing system for beginners. Now you can do your Trade yourself from anywhere
Open any web browser in your Mobile Phone or Laptop/Desktop. Write the PUJI OMS URL https://puji.fcslbd.com:8000 in address bar and hit enter.
You will get the login interface as follows
 Login Page
Login Page
Input your User ID and Password, Press login. After login you will get the screen as follows
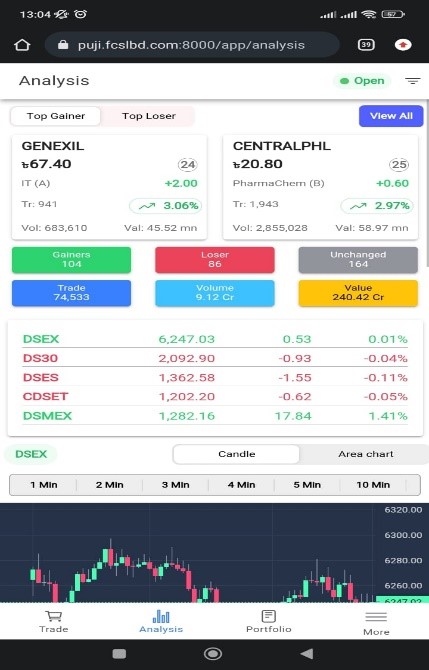 Analysis
Analysis
There are four buttons in the bottom of the screen
First one is Trade where you can submit your Buy/Sell order. Click on Buy or Sell option according to your need. Then Select Market type Public/Block/Debt, insert Quantity and Price. Press on “SUBMIT ORDER” button to place the Buy/Sell order. In the same screen you can see your Order List which can be sorted by All/Active/Executed/Terminated.
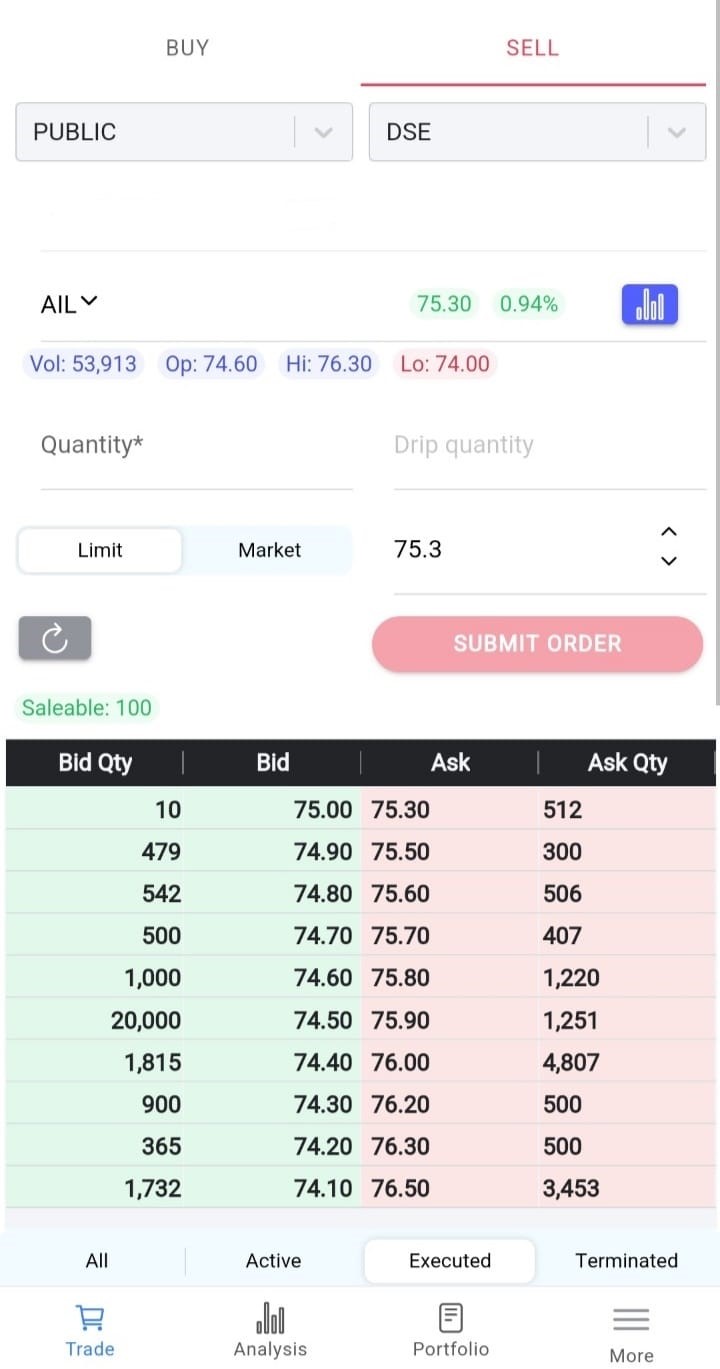 Trade
Trade
Second one is Analysis. Here by default Top Gainer/Top Loser, DSE indices (DSEX, DS30, DSES, CDSET, DSMEX), DSEX Graph (Candle & Area Chart), Top Sectors by Gainer, Top Sectors by Value.
If you want to see all share price together in screen then click to “View All” button located in Upper Right Corner of Analysis page. There are many sorting options, you may sort by Gainers, by Loser, by Value etc. Also there are many filtering options like Market, Boards etc. You may also change display layout.
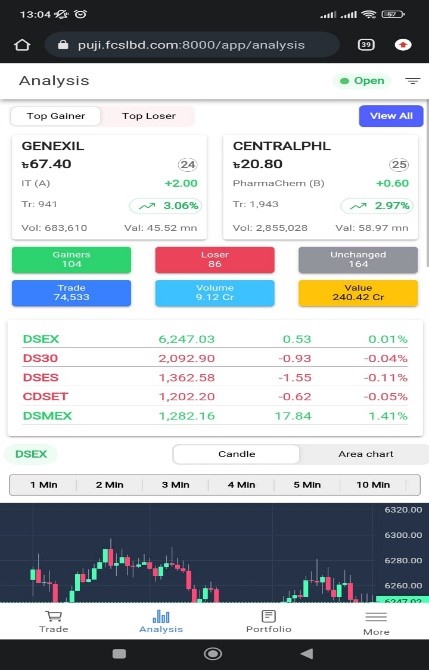 Analysis
Analysis
Third button is Portfolio. Here you can see your Purchase Power, Cash, Intraday Cash, and Purchased Share details etc.
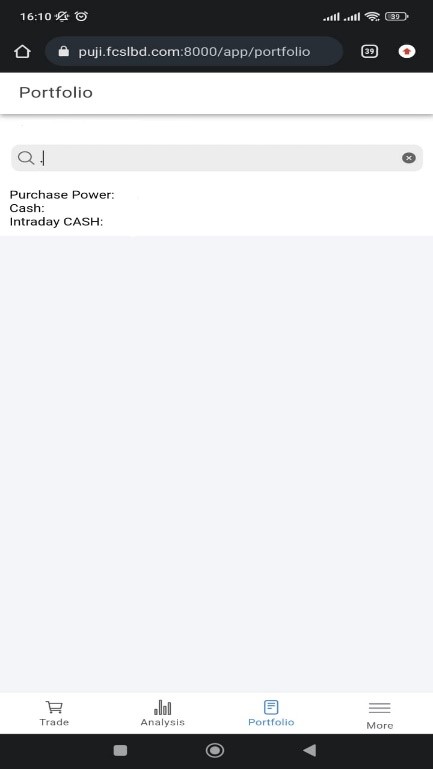 Portfolio
Portfolio
Forth button is Menu. In Menu list you will get Watch lists, Order list, About Us, Privacy Policy, Display Mode Change (Light Mode/Dark Mode), Change Password and Log out options.
In Watch Lists you can create multiple share list of your choice.
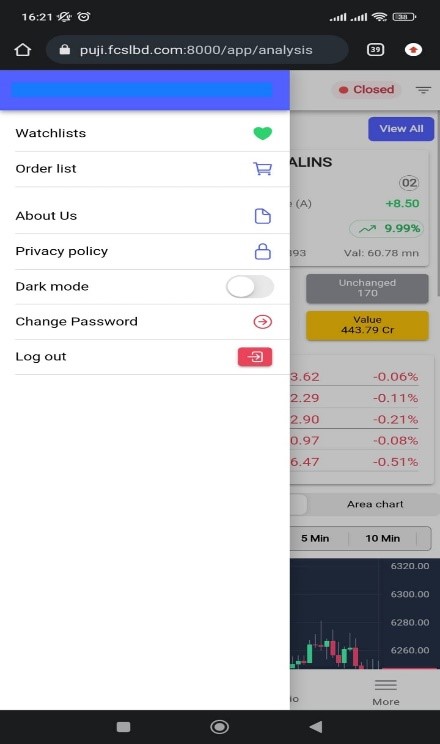 Menu
Menu